Mysql Mac Os X 10.6 Download
Get your Local Web Development Environment Up & Running on macOS Big Sur 11 and Catalina ten.15

With Apples' new macOS Big Sur 11 bachelor for download, here is how to get the AMP stack upwards and running on the new macOS. This tutorial will become through the procedure of getting Apache, MySQL, PHP (or otherwise known as the 'AMP' stack) and phpMyAdmin running on the new mac Bone Large Sur.
This guide volition too work on macOS Catalina and Mojave.
This tutorial sets up the AMP stack in more of a traditional way using the loaded Apache and PHP and downloading MySQL and phpMyAdmin.
Apache/WebSharing
Web serving is built into Big Sur with Apache app, it is installed ready to be fired upwards.
This needs to be done in the Terminal which is found in the Os filing organization at /Applications/Utilities/Concluding
For those not familiar with the Last, information technology really isn't as intimidating as you may call up, in one case launched y'all are faced with a control prompt waiting for your commands - just type/paste in a command and hit enter, some commands requite you lot no response - it just means the command is done, other commands give y'all feedback.
Using the prefix of sudo is required for commands that accept their applications protected in specific folders - when using sudo yous volition need to confirm with your admin password or iCloud password if set upward that fashion.... permit'southward get to information technology ...
to start Apache web sharing
sudo apachectl offset
to cease it
sudo apachectl stop
to restart it
sudo apachectl restart
To find the Apache version
httpd -v
The Apache version that comes in macOS Big Sur is Apache/2.iv.46
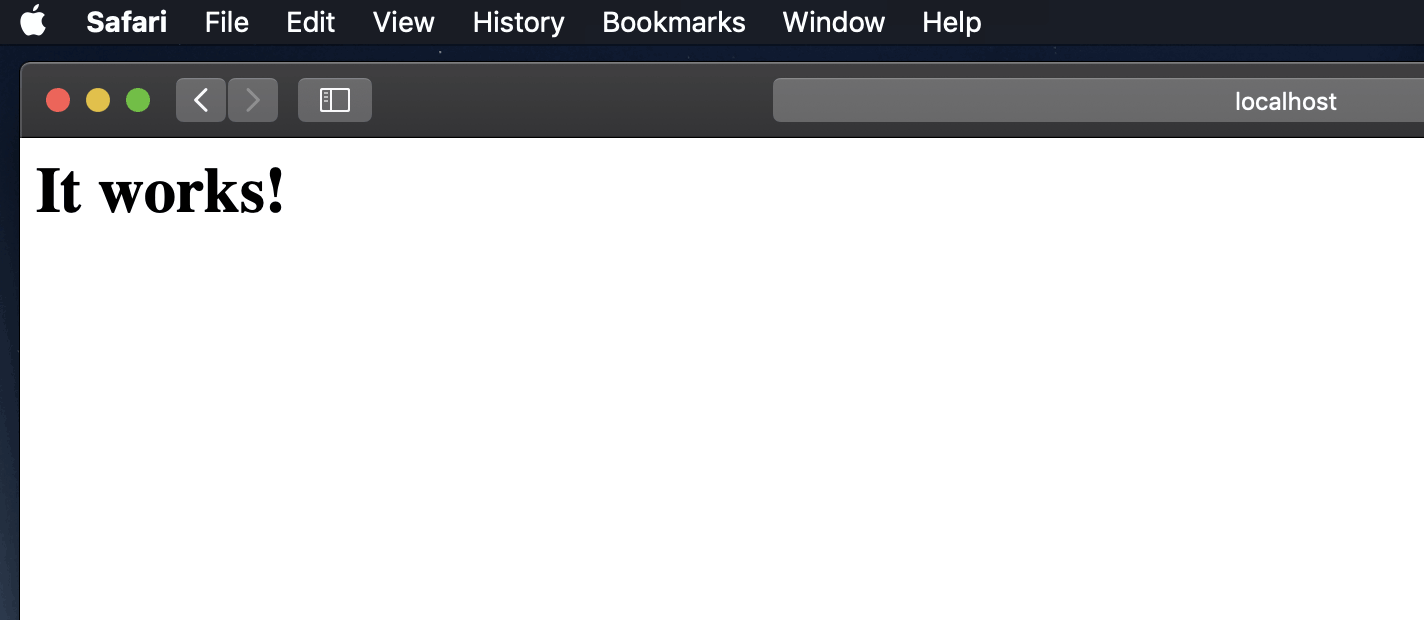
After starting Apache - test to see if the webserver is working in the browser - http://localhost - you should see the "Information technology Works!" text.
If you don't get the localhost exam, you tin try troubleshooting Apache to come across if at that place is anything incorrect in its config file by running
apachectl configtest
This will give you an indication of what might be incorrect.
Document Root
Document root is the location where the files are shared from the file organization and is similar to the traditional names of 'public_html' and 'htdocs', macOS has historically had two web roots one at a system level and one at a user level - you tin can ready both up or just run with one, the user level one allows multiple accounts to have their own web root whilst the organisation i is global for all users. Information technology seems in that location is less effort from Apple in standing with the user level one but it still can be set with a couple of actress tweaks in configuration files. It is easier to use the user level one as you don't have to proceed on authenticating equally an admin user.
Arrangement Level Web Root
- the default system document root is still plant at -
http://localhost/
The files are shared in the filing system at -
/Library/WebServer/Documents/
User Level Root
The other web root directory which is missing by default is the '~/Sites' folder in the User account. This takes a bit longer to prepare but some users are very accustomed to using it.
Yous demand to make a "Sites" folder at the root level of your account and and so it will work. Once you brand the Sites binder you will notice that information technology has a unique icon which is a throwback from a few versions older. Make that folder before you set up the user configuration file described next.
You accept to brand a few additional tweaks to become the ~/Sites binder support and running.
Add a "username.conf" filed nether:
/etc/apache2/users/
If yous don't already accept one (very likely), so create i named past the brusk username of the account with the suffix .conf, its location and permissions/ownership is all-time tackled by using the Concluding, the text editor 'nano' would exist the best tool to deal with this.
If you would rather edit config files in a text editor every bit an app I would suggest text editor like the free BBEdit which allows you to open hidden system files.

Launch Last, (Applications/Utilities), and follow the commands below, first one gets you to the correct spot, 2nd i opens the text editor on the command line (swap 'username' with your account's shortname, if you don't know your account shortname type 'whoami' the Terminal prompt):
cd /etc/apache2/users
sudo nano username.conf
Then add the content beneath swapping in your 'username' in the code below, there is a slightly dissimilar user directive for Big Sur and Catalina, make certain 'Require host localhost' is used:
<Directory "/Users/username/Sites/"> AllowOverride All Options Indexes MultiViews FollowSymLinks Require host localhost </Directory>
Permissions on the file should be:
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 298 Jun 28 16:47 username.conf
If not, you need to change information technology...
sudo chmod 644 username.conf
Open up the chief httpd.conf and allow some modules:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/httpd.conf
And make sure these modules are uncommented (the offset 2 should already be on a clean install):
LoadModule authz_core_module libexec/apache2/mod_authz_core.so
LoadModule authz_host_module libexec/apache2/mod_authz_host.so
LoadModule userdir_module libexec/apache2/mod_userdir.so
LoadModule include_module libexec/apache2/mod_include.then
LoadModule rewrite_module libexec/apache2/mod_rewrite.so
While you lot have this file open also to go php running, uncomment the below ... (Mentioned besides in the PHP part of the article).
LoadModule php7_module libexec/apache2/libphp7.so
And likewise uncomment this configuration file as well in httpd.conf - which allows user habitation directories.
Include /private/etc/apache2/extra/httpd-userdir.conf
Relieve all your changes (Control + O in nano)
Then open some other Apache config file and uncomment another file:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/extra/httpd-userdir.conf
And uncomment:
Include /private/etc/apache2/users/*.conf
Relieve all your changes (Command + O in nano)
Restart Apache for the new file to be read:
sudo apachectl restart
And so this user level document root volition be viewable at:
http://localhost/~username/
You should only see a directory tree like structure if the folder is empty.
Override .htaccess and allow URL Rewrites
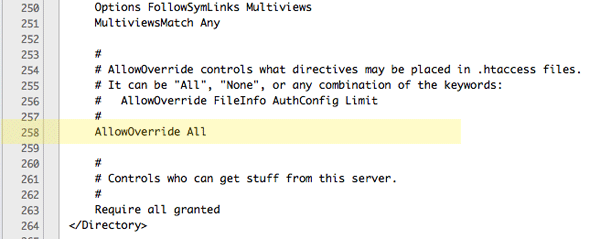
If you are going to use the spider web serving document root at /Library/WebServer/Documents it is a good thought to allow any .htaccess files used to override the default settings - this can be achieved by editing the httpd.conf file at line 217 and setting the AllowOverride to All and so restart Apache. This is already taken intendance of at the Sites level webroot past post-obit the previous pace.
sudo nano /etc/apache2/httpd.conf
Also while here allow URL rewrites then your permalinks look clean, not ugly.
Uncomment in httpd.conf - should be uncommented on a make clean install.
LoadModule rewrite_module libexec/apache2/mod_rewrite.so
PHP
PHP seven.3.24 is loaded in this version of macOS Big Sur and needs to be turned on by uncommenting a line in the httpd.conf file.
sudo nano /etc/apache2/httpd.conf
Use "control" + "w" to search inside nano and search for 'php' this will state you lot on the right line then uncomment the line (remove the #):
LoadModule php7_module libexec/apache2/libphp7.so
Write out and Save using the nano shortcut keys at the lesser 'command o' and 'command x'
Reload Apache to kicking in
sudo apachectl restart
To see and examination PHP, create a file name it "phpinfo.php" and file it in your document root with the contents below, then view information technology in a browser.
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
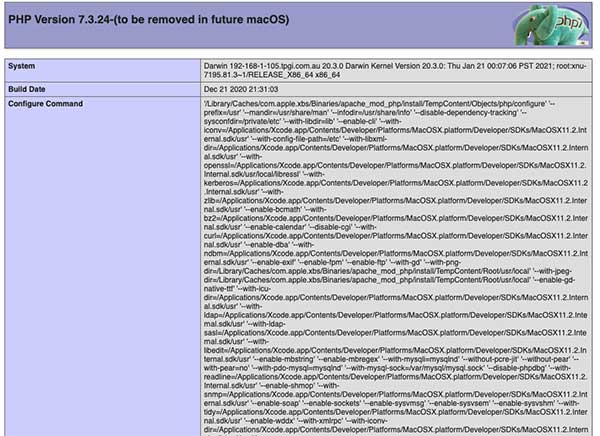
Here you will see that Apple tree are not intending on bundling PHP in the macOS in the hereafter, possibly with the next incarnation of the Bone, but for now information technology's working albeit not version vii.iv. Nonetheless yous can utilize a Homebrew PHP solution that allows for any PHP version to be used.
[email protected] Documents % php -5 WARNING: PHP is not recommended PHP is included in macOS for compatibility with legacy software. Future versions of macOS will not include PHP. PHP 7.three.24-(to be removed in future macOS) (cli) (built: Dec 21 2020 21:33:25) ( NTS ) Copyright (c) 1997-2018 The PHP Grouping Zend Engine v3.iii.24, Copyright (c) 1998-2018 Zend Technologies
MySQL
MySQL doesn't come pre-loaded with macOS Big Sur and needs to be dowloaded from the MySQL site.
The latest version of MySQL 8.0.23 does work with the latest release of macOS.
Use the macOS x.15 (x86, 64-chip), DMG Archive version (works on macOS Big Sur).
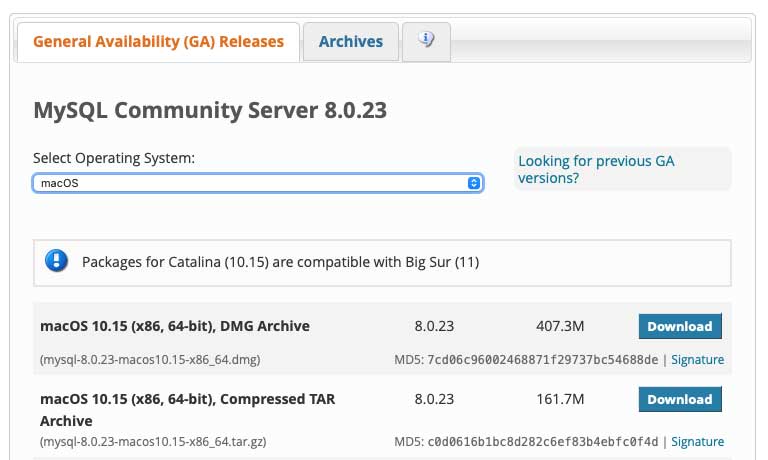
If you lot are upgrading from a previous macOS and accept an older MySQL version you do not have to update it.
Also if you have a clean install and desire the earlier MySQL version 5.vii, you can still get this from the MySQL site - from the 'Looking for previous GA versions' link. (MySQL viii is relatively new and not in many production prepare ups)
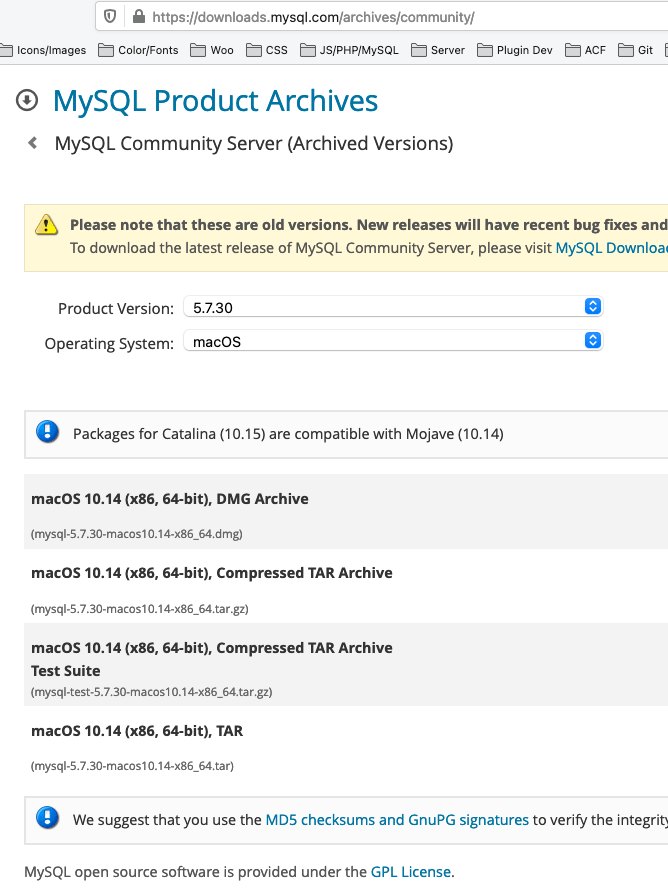
I thing with MySQL upgrades, always take a information dump of your database in case things get south and before you upgrade to macOS Catalina make certain your MySQL Server is not running.
When downloading you don't take to sign up, wait for » No thank you, just starting time mydownload - become directly to the download.
One time downloaded open the .dmg and run the installer.
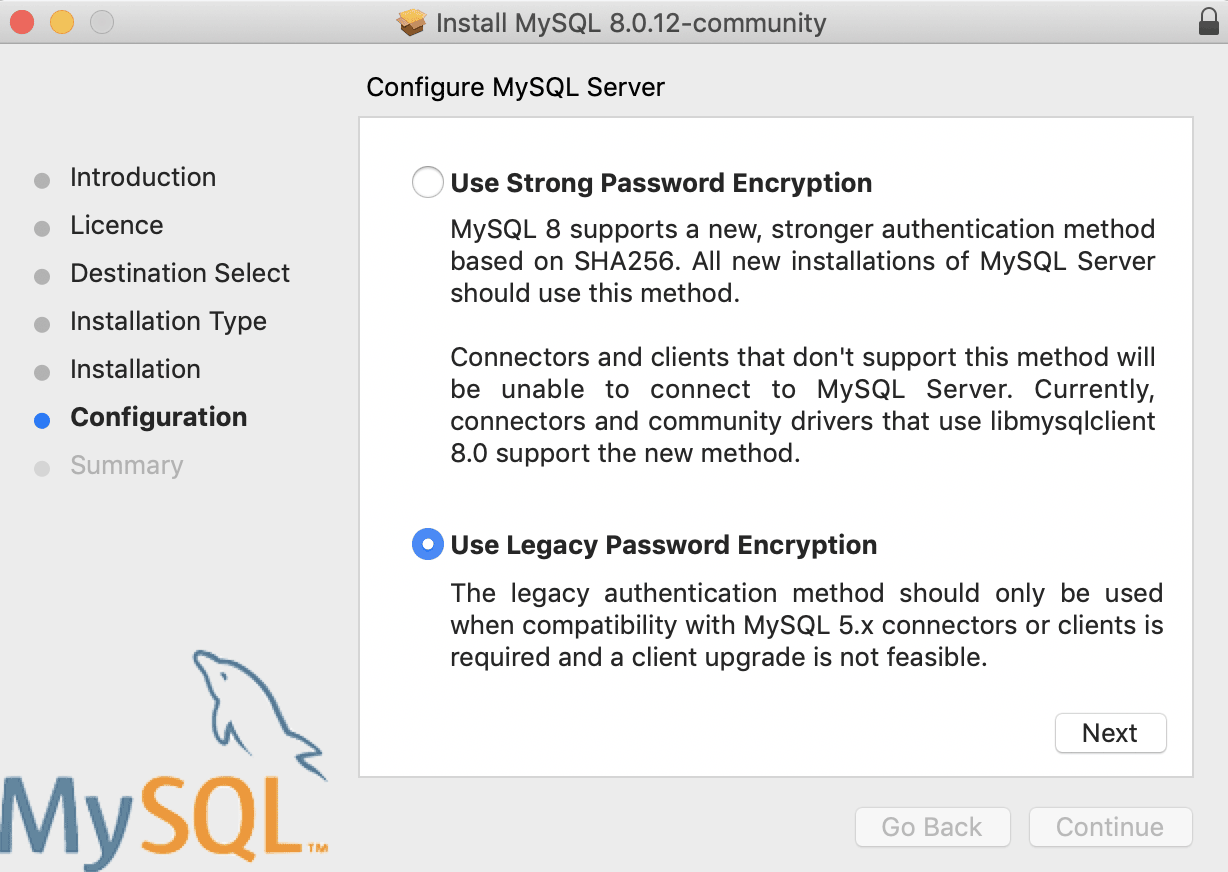
During the MySQL process you are prompted to choose between strong and legacy password encryptions, since version viii is entirely new, some software like phpMyAdmin can't connect with the newer encryptions - so if yous are going to employ a GUI wrapper like phpMyadmin I suggest yous stick to legacy.
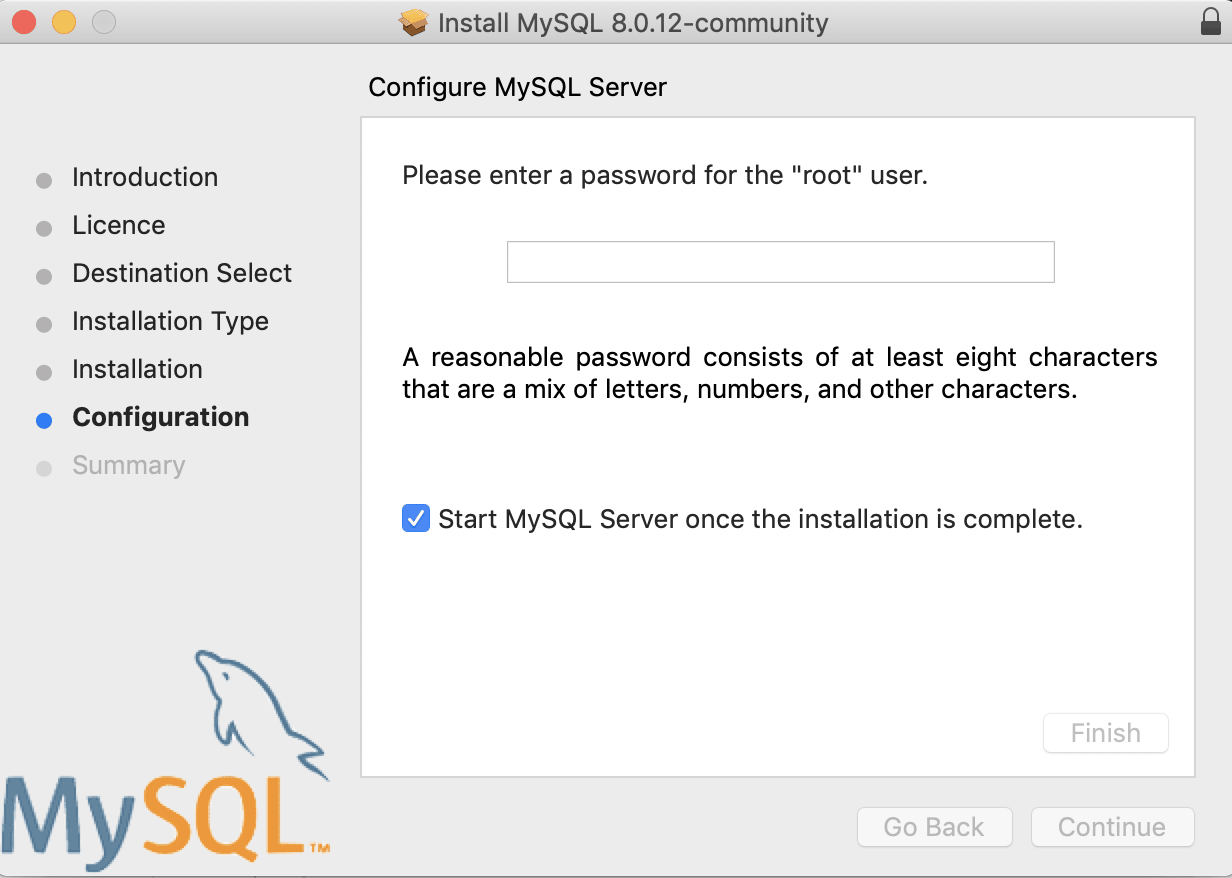
And then add a password for the MySQL root user.
Add Mysql to your path
After installation, in order to utilise MySQL commands without typing the full path to the commands you demand to add the mysql directory to your shell path, (optional step) this is washed in your Zsh crush contour ".zshrc" file in your home directory (previous shells were bash ), if you don't have that file just create information technology using 6 or nano:
cd ; nano .zshrc
export PATH="/usr/local/mysql/bin:$PATH"
The first command brings you to your dwelling house directory and opens the .zsh file or creates a new i if information technology doesn't exist, then add in the line above which adds the MySQL binary path to commands that you can run. Exit the file with type "command + 10" and when prompted to save the modify by typing "y". The last thing to do hither is to reload the shell for the above to work straight away.
source ~/.zshrc
Change the MySQL root countersign
(This section is left in for reference - in previous macOS MySQL packages the countersign prepare during the installation procedure would fail - hence the info below. This newer version, nevertheless, seems to work).
Note that this is not the same every bit the root or admin password of macOS - this is a unique countersign for the MySQL root user.
Terminate MySQL
sudo /usr/local/mysql/back up-files/mysql.server stop
Start it in safe way:
sudo mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables
This will be an ongoing control until the procedure is finished and then open another shell/final window, and log in without a password as root:
mysql -u root
Flush PRIVILEGES;
Alter USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED Past 'MyNewPass';
Change the lowercase 'MyNewPass' to what you desire - and keep the unmarried quotes.
\q
Starting time MySQL
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server start
Starting MySQL
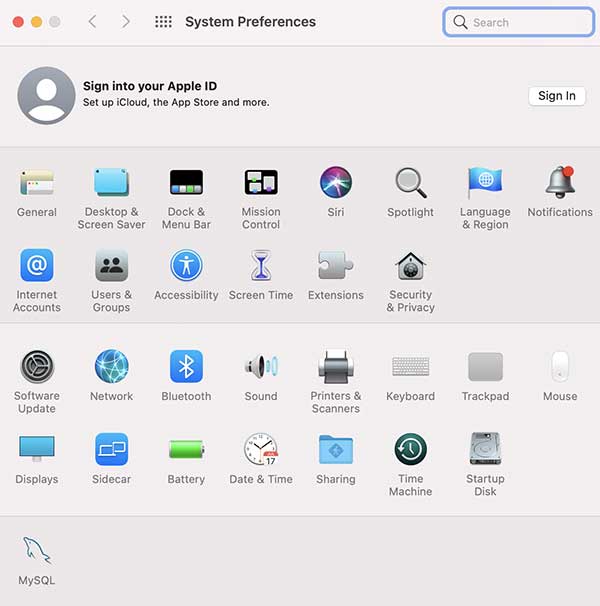
You tin can and then get-go the MySQL server from the Organisation Preferences adds to the terminal row or via the command line.
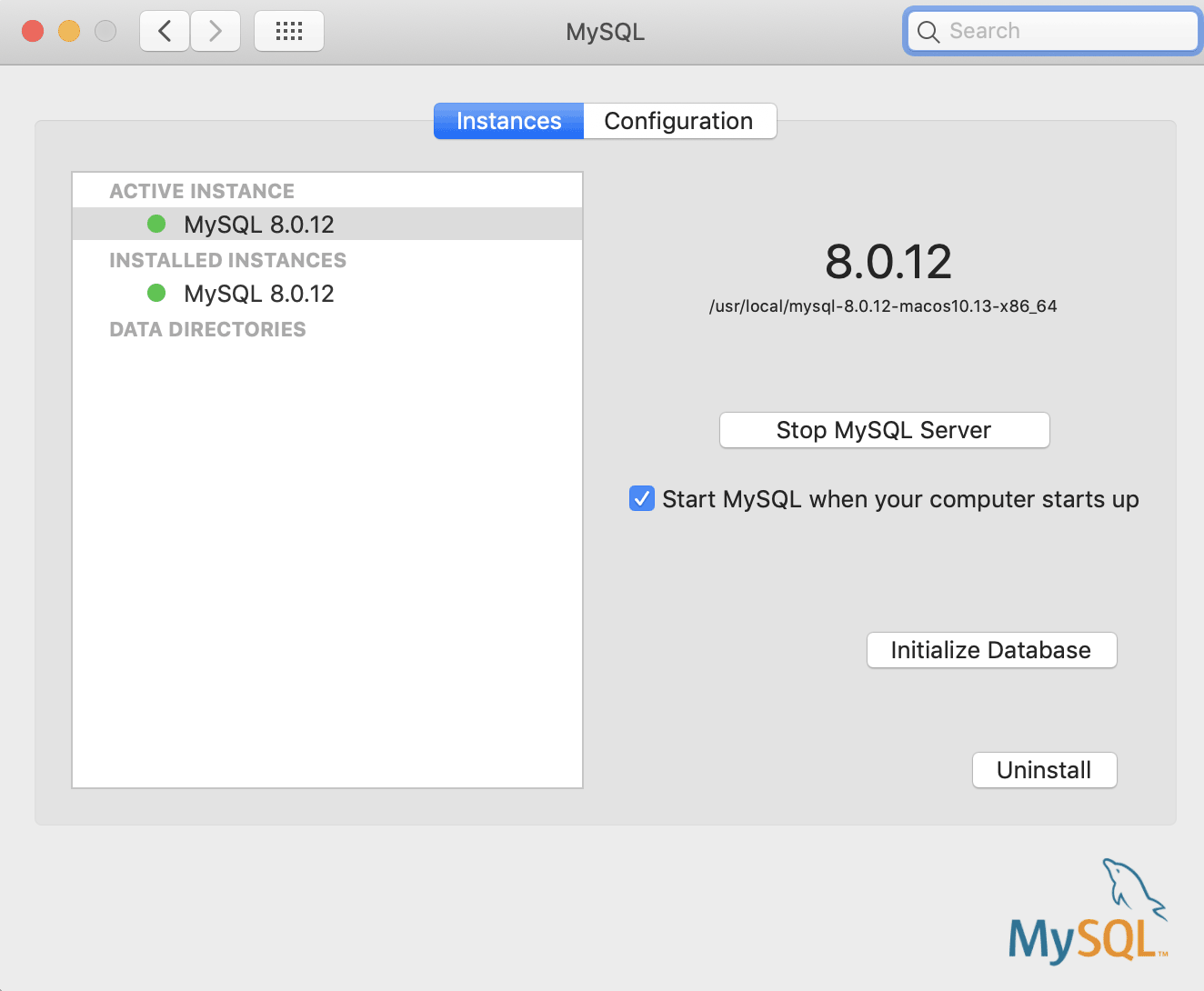
The new MySQL arrangement preference also has the uninstall characteristic - useful if you've installed it with a security encryption that's non working for y'all and want to try the other one. Yous can also meet the paths to the config and data sources of MySQL in the configuration tab.
Or to Control line start MySQL.
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server start
To discover the MySQL version from the last, type at the prompt:
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql -v -uroot -p
This as well puts you into a beat interactive dialogue with MySQL, type \q to exit.
Fix the 2002 MySQL Socket error
Fix the looming 2002 socket mistake - which is linking where MySQL places the socket and where macOS thinks it should exist, MySQL puts it in /tmp and macOS looks for information technology in /var/mysql the socket is a type of file that allows MySQL customer/server communication.
sudo mkdir /var/mysql
sudo ln -s /tmp/mysql.sock /var/mysql/mysql.sock
phpMyAdmin
Outset set up the 2002 socket fault if yous haven't done so from the MySQL section-
sudo mkdir /var/mysql
sudo ln -due south /tmp/mysql.sock /var/mysql/mysql.sock
Download phpMyAdmin, the zip English package will arrange a lot of users, then unzip it and move the binder with its contents into the document root level renaming folder to 'phpmyadmin'.
Make the config folder
mkdir ~/Sites/phpmyadmin/config
Change the permissions
chmod o+w ~/Sites/phpmyadmin/config
Run the gear up upward in the browser
http://localhost/~username/phpmyadmin/setup/ or http://localhost/phpmyadmin/setup/
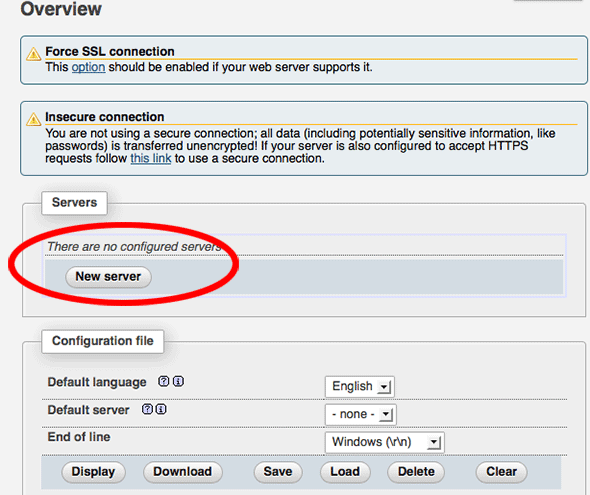
You need to create a new localhost mysql server connection, click new server.
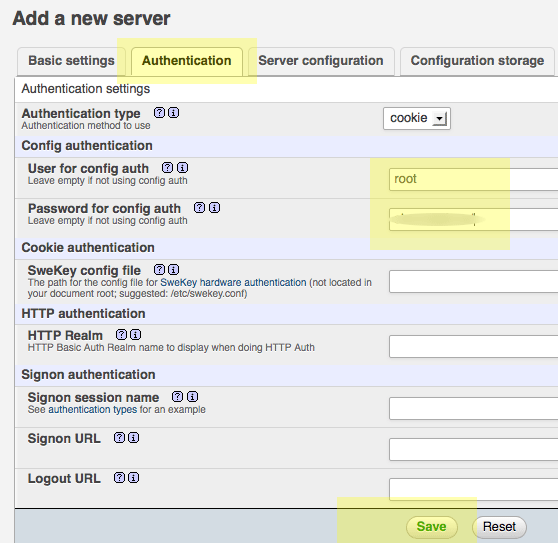
Switch to the Authentication tab and set the local MySQL root user and the password.
Add in the username "root" (possibly already populated, add in the password that you fix up before for the MySQL root user set, click on save and you are returned to the previous screen.
(This is not the macOS Admin or root password - it is the MySQL root user)
Now going to http://localhost/~username/phpmyadmin/ will now permit you to interact with your MySQL databases.
Permissions
To run a website with no permission issues information technology is best to set the web root and its contents to be writeable by all since it's a local development information technology shouldn't exist a security issue.
Let's say that y'all take a site in the User Sites binder at the following location ~/Sites/testsite y'all would fix it to be writeable similar so:
sudo chmod -R a+w ~/Sites/testsite
If you are concerned about security so instead of making it world writeable you can prepare the owner to exist Apache _www simply when working on files you would have to cosign more as admin you are "not" the owner, you would practice this like so:
sudo chown -R _www ~/Sites/testsite
This will set the contents recursively to be endemic by the Apache user.
If yous had the website stored at the System level Document root at say /Library/WebServer/Documents/testsite then it would have to be the latter:
sudo chown -R _www /Library/WebServer/Documents/testsite
Another more straightforward fashion to practise this if yous have a one user workstation is to modify the Apache web user from _www to your business relationship.
That's it! You now have the native AMP stack running on peak of macOS Big Sur or Catalina.
To fix vritual hosts aka vhosts on Apache cheque the guide here.
If y'all are a WordPress user and desire a smooth lean local evolution environs - too worth checking out is Laravel Valet which runs on top of macOS - bank check out my Valet WordPress Guide on macOS.
Mysql Mac Os X 10.6 Download
Posted by: nelsonbale1939.blogspot.com

0 Comentarios